
|
|
- Technical Information
- Drill features and specification
- Cutting edge geometry and its influence
DRILL FEATURES AND SPECIFICATION
CUTTING EDGE GEOMETRY AND ITS INFLUENCE
As shown in the table below, it is possible to select the most suitable cutting edge geometry for different applications. If the most suitable cutting edge geometry is selected then higher machining efficiency and higher hole accuracy can be obtained.
Cutting Edge Shapes
| Grinding name | Shape | Features and effect | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conical | 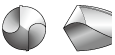 |
|
|
| Flat | 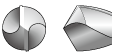 |
|
|
| Three flank angles | 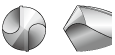 |
|
|
| Spiral point | 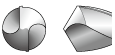 |
|
|
| Radial lip | 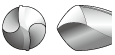 |
|
|
| Centre Point drill | 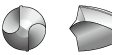 |
|
|