
 BACK BACK |
- Technical Information
- Reference
- Function of Tool Features for Face Milling
- Corner Angle(CH) and Cutting Resistance
FUNCTION OF TOOL FEATURES FOR FACE MILLING
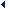
CORNER ANGLE (CH) AND CUTTING RESISTANCE
Cutting Resistance Comparison between
Different Insert Shapes
Different Insert Shapes
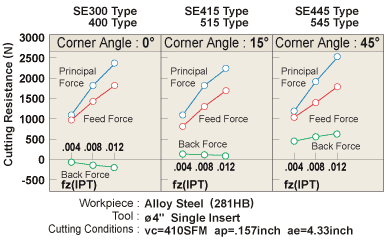
Three Cutting Resistance Forces in Milling
Corner Angle 0° |
Back force is in the minus direction. Lifts the workpiece when workpiece clamp rigidity is low. |  |
Corner Angle 15° |
Corner angle 15° is recommended for face milling of workpieces with low rigidity such as thin workpieces. | 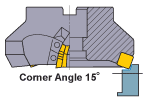 |
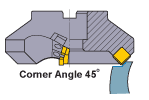
Corner Angle 45° |
The largest back force. Bends thin workpieces and lowers cutting accuracy. * Prevents workpiece edge chipping in cast iron cutting. |
 |
- Principal force: Force is in the opposite direction of face milling rotation.
- Back force: Force that pushes in the axial direction.
- Feed Force: Force is in the feed direction and is caused by table feed.